Advanced Infrastructure Materials and Manufacturing Lab
Summary
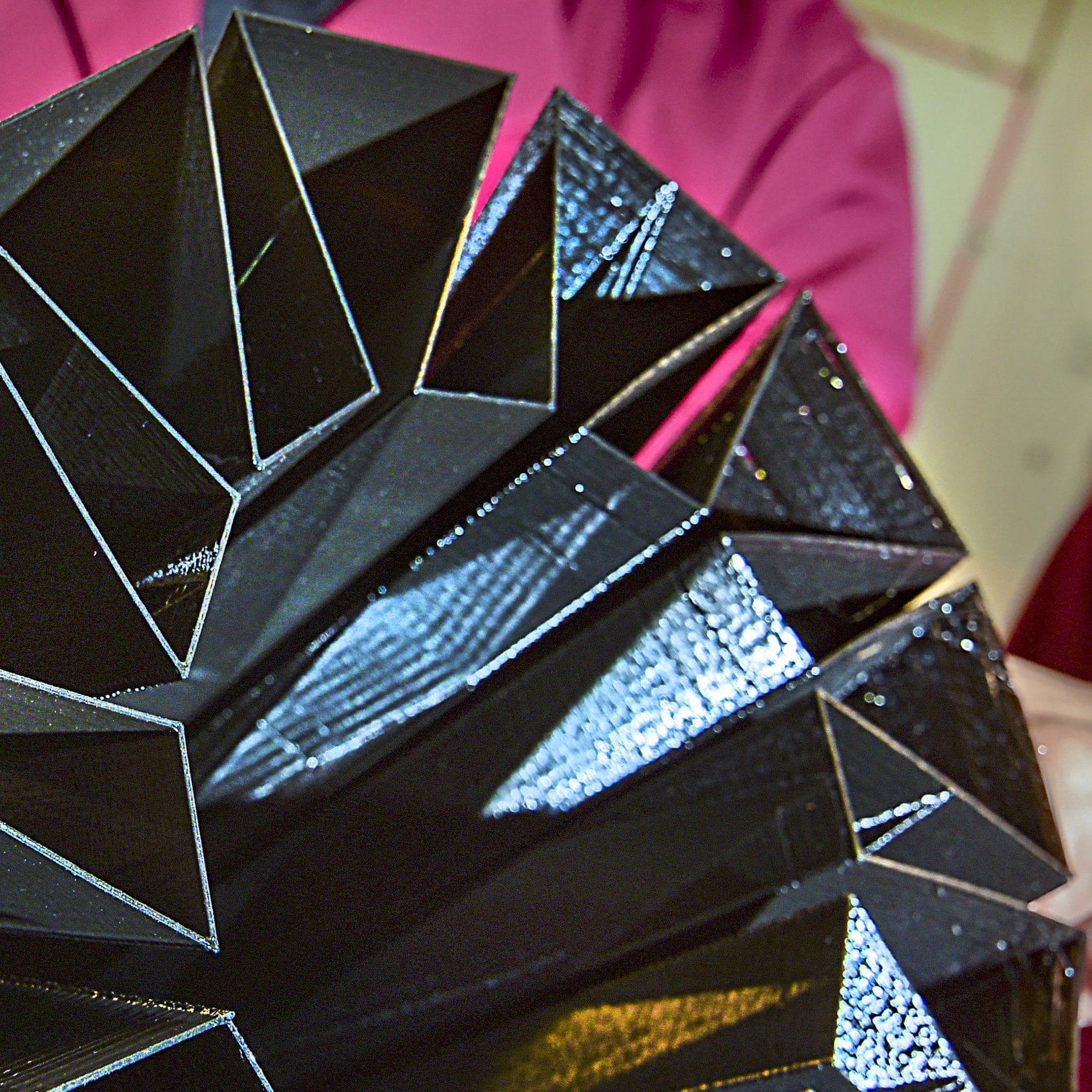

One thing we know for sure: the future of infrastructure will not look like its past. The main strength of this cross-disciplinary lab is to bridge the recent advancements in additive manufacturing technologies with large-scale structures. The Advanced Infrastructure Materials & Manufacturing (AIMM) Lab focuses on developing advanced, symbiotic and conjoint materials and manufacturing methods, including applications of robotics and 3-D printing in additive manufacturing technology. More efficient than conventional construction methods, these new methods can yield less material waste, greater quality and better on-site safety. The AIMM lab is shifting not only how infrastructure is constructed today, but also transforming the way infrastructure is designed and built in the future from beginning to end.
Research
- Investigate laser-assisted robotic 3D printing on freeform surfaces with different nature-inspired structures.
- Explore a process that may serve as a prototype for future robotic 3D printing, capable of following and printing a pattern overlaid on any surfaces (e.g., predesigned substrates or existing surfaces).
- 3D printing of infrastructure components and sub-systems.
- 3D printing-enabled prognostics and health management (e.g. through embedding sensors during printing).
- Development of materials optimized for 3D printing.
Capabilities
- Multi-axis industrial robotic arm that:
- Benefits software and materials development to 3D print large-scale structures for infrastructure applications.
- Can scan the surface and repair it (applicable to robotic road repair that can save material costs and keep workers out of danger).
- Delta WASP 4070 3D printer that:
- Is capable of printing polymer and clay materials.
- Can print polymers (PLA, ABS, TPU, PETG) filaments via the FDM process.
- Can print cementitious/clay-like materials via the material extrusion process.
Lab Supervisors:

Dr. Petros Sideris
Associate Professor, Civil & Environmental Engineering
[email protected]
979-845-2708

Dr. Yong-Rak Kim
Professor, Zachry Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering
[email protected]
979-847-7366